Control of metabolic function through protein phosphorylation
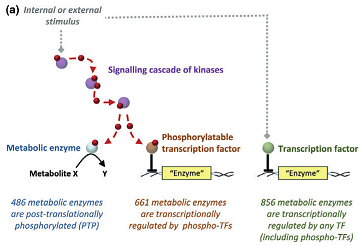
Overwhelming evidence suggests that microbes use transcription mainly to allocate protein resources but rarely to make executive decisions on usage of pathways or the extent of flux through them. Allosteric regulation and protein phosphorylation are two likely molecular mechanism to implement pathway choice and rate decisions, but both fields are underdeveloped. Although phosphoproteomic data increasingly populate databases, the functional relevance of individual phosphorylation events is mostly unknown. For example, more than half of the about 1000 yeast enzymes are known to be phosphorylated, but only 24 phosphorylation events are functionally validated to control enzyme activity.
In close collaboration with the Aebersold lab we combine phosphoproteomics with metabolomics and flux analysis to infer functionality of phosphoregulation on a larger scale. Key applications are TORC1 regulation in yeast (external pageSignalXcall_made project) and microbial central metabolism.
References
- Schastnaya E, Doubleday P, Maurer L & Sauer U (2023). Non-enzymatic acetylation inhibits glycolytic enzymes in Escherichia coli. Cell Rep, 42, 111950. external pagehttps://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2022.111950call_made
- Schastnaya E, Raguz Nakic Z, Gruber C, Doubleday P, Krishnan A, Johns N, Park J, Wang H & Sauer U (2021). Extensive regulation of enzyme activity by phosphorylation in Escherichia coli. Nat Comms, 12, 5650. external pagehttps://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-25988-4call_made
- Gruber C, Diether M & Sauer U (2021). Conservation of metabolic regulation by phosphorylation and non-covalent small-molecule interactions. Cell Sys, 12, 6, 538-546. external pagehttps://doi.org/10.1016/j.cels.2021.04.009call_made
- Kochanowski K, Sauer U & Chubukov V (2013). Somewhat in control – the role of transcription in regulating microbial metabolic fluxes. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 24: 987-933.
- Robitaille AM, Christen S, Shimobayashi M, Cornu M, Fava LL, Moes S, Prescianotto-Baschong C, Sauer U, Jenoe P & Hall MN (2013). Quantitative phosphoproteomics reveal mTORC1 activates de novo pyrimidine synthesis. Science 339:1320-3.
- Oliveira AP, Ludwig C, Picotti O, Kogadeeva M, Aebersold R & Sauer U (2012). Regulation of yeast central metabolism by enzyme phosphorylation. Mol Sys Biol. 8: 623.
- Oliveira AP & Sauer U (2012). The importance of post-translational modifications in regulating S. cerevisiae metabolism. FEMS Yeast Res. 12:104-17.
